With the transition to digital communication and more frequent work from home, the number of cyberattacks on companies is increasing. Recently, the number of so-called phishing attacks has increased at an unprecedented rate.
All fake e-mails are a form of social engineering designed to solicit information from users. Technically, an attack using social engineering can be considered an attack that requires human interaction to obtain information about or compromise the victim. An attacker can impersonate IT support staff, a new employee, a service provider, and so on.
The goal of phishing may not only be to obtain data, but also to support further attacks. Of course, the attackers also use current events from around the world and try to adapt to them. Favourites include natural disasters (droughts, floods), epidemics (many phishing e-mails or sites have appeared in connection with COVID-19), elections, holidays or data update requests.
How to identify an attack?
• Suspicious sender's address - Check the sender's address carefully, as the address may look legitimate at first glance. However, it may be in a non-standard format (characters are missing, bad formatting, etc.).
• Generated greetings or signatures - Generic greetings or signatures should also alert you. Examples include "Dear Sir/Madam" or "Dear Customer".
• Spurious hyperlinks or pages - This can be very well identified by placing the mouse cursor on the link and see which address it is pointing to. But it is important to be careful at this point. Addresses can be very similar to the correct addresses.
• Grammatical accuracy and appearance of the e-mail message - If the e-mail message contains incorrect grammar or unusual formatting, it is most likely a forged message.
• Suspicious attachments - Examples are unexpected attachments, calls for urgent download from a website, requests for urgent payment of an order you are not aware of, etc.
How best to defend yourself?
In general, from the point of view of cybersecurity the most important defences are analysis followed by training (and subsequent regular training) of users. There are solutions that allow you to send simulated attacks in the form of fake e-mails to targeted recipients. Subsequently, over time we will evaluate the reaction of users and propose measures. The simulated submission itself is also a form of training users how a targeted campaign against a given company can look like.
The process of the entire anti-phishing defence is as follows:
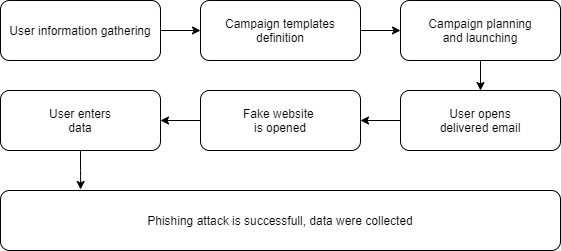
The entire campaign is implemented in several stages. First, the range of target recipients is defined and then they are targeted with the various campaigns. Each user will receive a fake e-mail according to a template that mimics e-mail messages from Microsoft or Google. Its purpose is to evoke in the user a sense of urgency to open an e-mail and enter data.
The next stage is the final evaluation of the information obtained and a proposal for further steps for the company. All data is processed completely anonymously and with respect for all users.
Due to the increasing number of attacks on companies worldwide as well as in our country, I strongly recommend focusing on cybersecurity in your company. Above all, the proverbial "prevention is always cheaper than a cure" applies here.